Get Your Free Quote
- Best Price Guarantee Buy with confidence because you aren't getting a better price than this.
- Free Shipping
Enjoy the luxury of free shipping on orders above $299. - A Grade Quality Used Car Parts
Avail the best OEM Auto parts & components that are just as new. - Our Friendly Parts Specialist will get you what you need !!
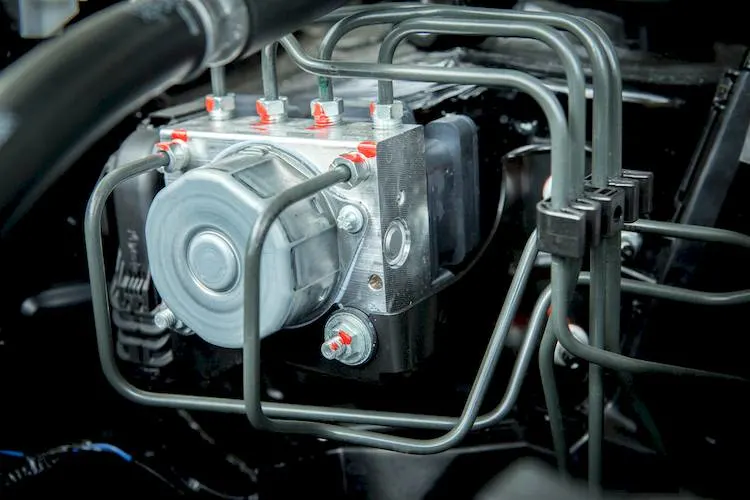
What is an ABS Pump and How Does It Work?
An ABS pump is a vital part of many modern braking systems. It is a component that helps to prevent the wheels from locking up and skidding when the driver applies the brakes hard or in slippery conditions. It does so by modulating the brake pressure to each wheel according to the signals from the wheel speed sensors and the ABS controller. In this article, we will explain what an ABS pump is, how it works, what are its advantages and disadvantages, and how to maintain it.
What is an ABS Pump?
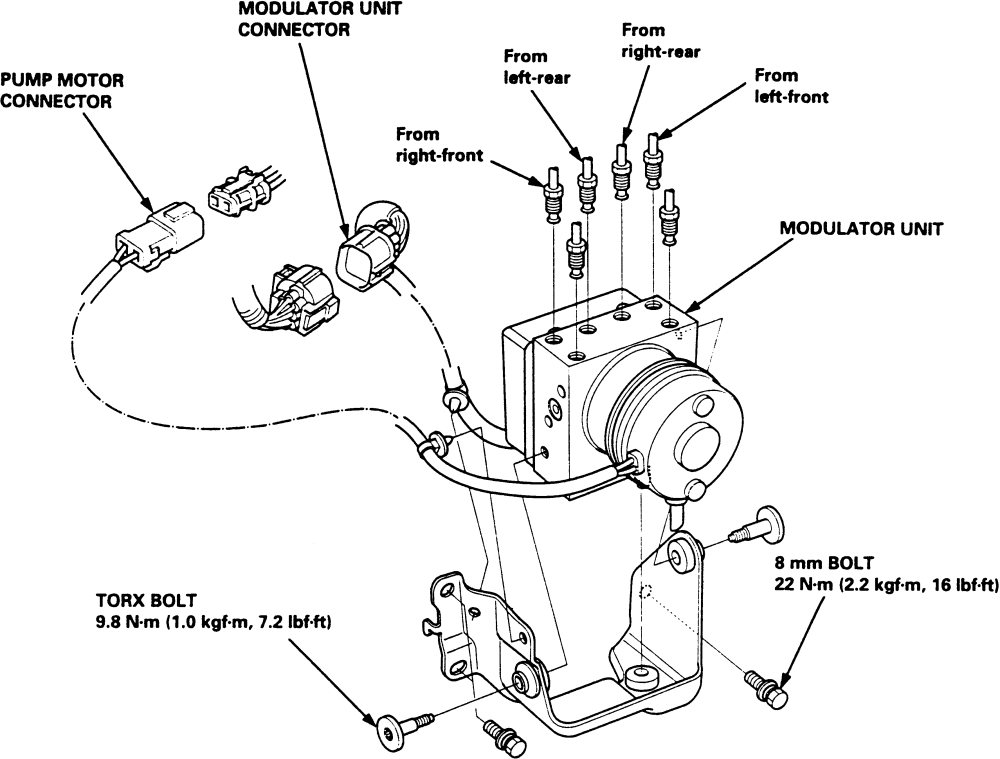
An ABS pump is also called the ABS modulator, Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU), or even ABS motor. It typically comprises an electrical motor, ABS valves operated by solenoids, and a base where brake hoses (from the master cylinder to brake calipers at each wheel) are connected.
The ABS pump is controlled by the ABS controller, which is also known as the ABS module or ABS ECU. The ABS controller is a computer that receives signals from the wheel speed sensors and other sensors, such as the brake pedal switch, the steering angle sensor, and the yaw rate sensor. The ABS controller then calculates the optimal brake pressure for each wheel and sends commands to the ABS pump to adjust the pressure accordingly.

How Does an ABS Pump Work?
The basic working principle of an ABS pump can be explained by following these steps:
- When the driver applies the brakes, the brake fluid pressure from the master cylinder reaches the ABS pump through the brake hoses.
- The ABS pump then distributes the brake fluid pressure to each wheel through the solenoid valves. The solenoid valves have three positions: open, closed, and partially open.
- The wheel speed sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel and send signals to the ABS controller.
- The ABS controller compares the wheel speed signals with a reference value and determines if any wheel is about to lock up or slip.
- If a wheel is about to lock up or slip, the ABS controller sends a command to the solenoid valve of that wheel to reduce or release the brake pressure. This allows the wheel to regain traction and avoid skidding.
- If a wheel needs more brake pressure, the ABS controller sends a command to the solenoid valve of that wheel to increase or restore the brake pressure. This allows the wheel to receive more braking force and stop faster.
- The ABS pump also uses its electric motor to restore the brake fluid pressure in the system after it has been released by the solenoid valves. This ensures that there is enough brake fluid pressure available for the next braking cycle.
- The ABS controller repeats these steps several times per second, depending on the driving conditions and the vehicle speed. This creates a pulsating sensation in the brake pedal, which indicates that the ABS system is working.
Advantages and Disadvantages of an ABS Pump
An ABS pump has some advantages and disadvantages compared to a conventional braking system. Some of them are:
Advantages-
- An ABS pump improves vehicle safety and stability by preventing wheel lock-up and skidding in hard braking situations or slippery road conditions.
- This allows - An ABS pump reduces the driver to maintain steering control and direction of the vehicle, the stopping distance of the vehicle by optimizing the brake pressure for each wheel according to the traction available.
- An ABS pump prevents tire wear and damage caused by excessive friction from locked or slipping wheels.
Disadvantages-
- An ABS pump increases the cost and complexity of the braking system, as it requires more components, wiring, and maintenance.
- An ABS pump can malfunction or fail due to various reasons, such as faulty sensors, valves, motor, or controller; low brake fluid level; air in the brake lines; or corrosion or damage in the system. This can compromise the braking performance and safety of the vehicle.
- An ABS pump can increase the noise level of the braking system, as it produces a humming or buzzing sound when it operates.
How to Maintain an ABS Pump-
An ABS pump requires regular inspection and service to ensure its proper functioning and reliability. Some of the maintenance tips are:
- Check the brake fluid level and condition regularly and refill or change it if needed. Use only the recommended type and grade of brake fluid for your vehicle.
- Bleed the air out of the brake system periodically or whenever you notice a spongy or soft brake pedal feel. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions on how to bleed the brakes with an ABS system.
- Clean and inspect the wheel speed sensors and their wiring for any dirt, debris, corrosion, or damage. Replace any faulty or damaged sensors or wires.
- Scan and diagnose the ABS controller for any trouble codes or warning lights. Use a compatible OBD-II scanner or take your vehicle to a professional mechanic for diagnosis and repair.
- Test and replace the ABS pump if it fails or shows signs of failure, such as unresponsive brake pedal, brakes locking up, or ABS warning light staying on. The ABS pump is usually located under the hood, near the firewall, or under the vehicle, near the fuel tank. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions on how to remove and install the ABS pump.
Are you looking for a Used Abs Control Module or Abs Pump Reach Us (786) 550-5786